Question 3: Explain Newton’s Laws of motion. Give examples in each case for further elaboration.
Answer
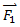 ,
, 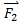 , …,
, …,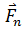 . If the sum of the forces is zero, there would be no unbalanced or net force acting on the body.
. If the sum of the forces is zero, there would be no unbalanced or net force acting on the body.
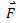 and
and 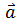 have the same direction.
When the direction of motion of body and the net force acting on it is the same, acceleration is said to be positive and the body speeds up. On the other hand, if the direction of motion and the direction of applied force are is opposite, the acceleration is negative and the body slows down.
Example
When a footballer kicks the ball, we can see easily that;
have the same direction.
When the direction of motion of body and the net force acting on it is the same, acceleration is said to be positive and the body speeds up. On the other hand, if the direction of motion and the direction of applied force are is opposite, the acceleration is negative and the body slows down.
Example
When a footballer kicks the ball, we can see easily that;
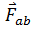 on body B. The law states this force of A on B,
on body B. The law states this force of A on B, 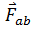 is the action of A on B. As a result, body B will also exert an equal opposite force
is the action of A on B. As a result, body B will also exert an equal opposite force 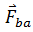 on body A. This force is called the reaction of B on A. So, according to the law,
on body A. This force is called the reaction of B on A. So, according to the law,
Newton’s First Law of Motion
In the absence of an external unbalanced force, if a body is at rest, will remain at rest, and if moving with uniform velocity, will continue to do so for ever. Now if a body is under the influence of a number of forces,∑F = Fnet = 0
The law states that under such conditions, the body will not change its state of rest or uniform motion. So the acceleration will be zero. Hence,![]()
Newton’s Second Law of Motion
When a certain net force is acting on a body, it produces acceleration in the body in its own direction. Moreover, the acceleration thus produced varies directly with the force and inversely with the mass of the body.![]()
- The ball goes faster if it is kicked harder and vice-versa. This means the acceleration produced is directly proportional to the applied force.
- The ball goes in the same direction in which it is kicked. This means the applied force of the kick produces acceleration in its own direction
Newton’s Third Law of Motion
It states that for every action there is always an equal but opposite reaction. Let we have two bodies A and B. Body A exerts a force![]() = –
= –![]()
- A direct conclusion of the law is that action and reaction always occur in pairs.
- Action and reaction never neutralize one another. They act on two different bodies. Only those equal forces balance one another which act on the same body.

Pingback:index-long-questions-ch3